Educational Information

Cataracts
Cataracts are the most common of vision loss in people over 40. Cataracts are the clouding of the lens inside of the eye causing blurry or hazy vision, glare, and/or change in glasses prescriptions. The only way to know for sure if you have cataracts is to have a comprehensive eye examination. For more information, click here.

Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a “silent blinder." It has no early warning sign and can be detected only with the comprehensive eye exam. Glaucoma damages the optic nerve, which carries information from the back of the eye to the brain. Tests done in assessing glaucoma might include checking the pressure inside the eye, visual fields, and photographs of the back of the eye. Progression of vision loss can be slowed down or stopped by eye drops and/or surgery. For more information, click here.
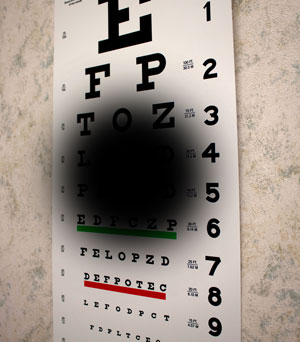
Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is an eye condition that effects the small central area of the back of the eye that is responsible for visual acuity. The health of the macula determines our ability to read, recognize faces, drive, watch TV, or other vision activities that require fine detail. It is the leading cause of vision loss in older Americans. Testing for macular degeneration includes a thorough retinal exam and may include visual fields, dark adaptation, and photography/OCT. For more information, click here.

Dry Eyes
Dry eyes are caused from lack of lubrication on the front surface of the eye. It is one of the most common eye conditions in the world. Consequences of dry eye can range from subtle, constant eye irritation to significant inflammation and even scarring of the front surface of the eye. Symptoms can include burning, itching, redness, blurring, red eyes, and even watery eyes. Dry eyes can be caused by insufficient oil production, causing tear evaporation or failure to produce enough tears. It can be influenced by environmental conditions, medication, computer use, contact lens wear, and many other factors. Treatment may include artificial tears, prescription medications, and in-office procedures like Blephex, all designed to help your body create and secrete more tears and decrease eye irritation and inflammation. For more information, click here.
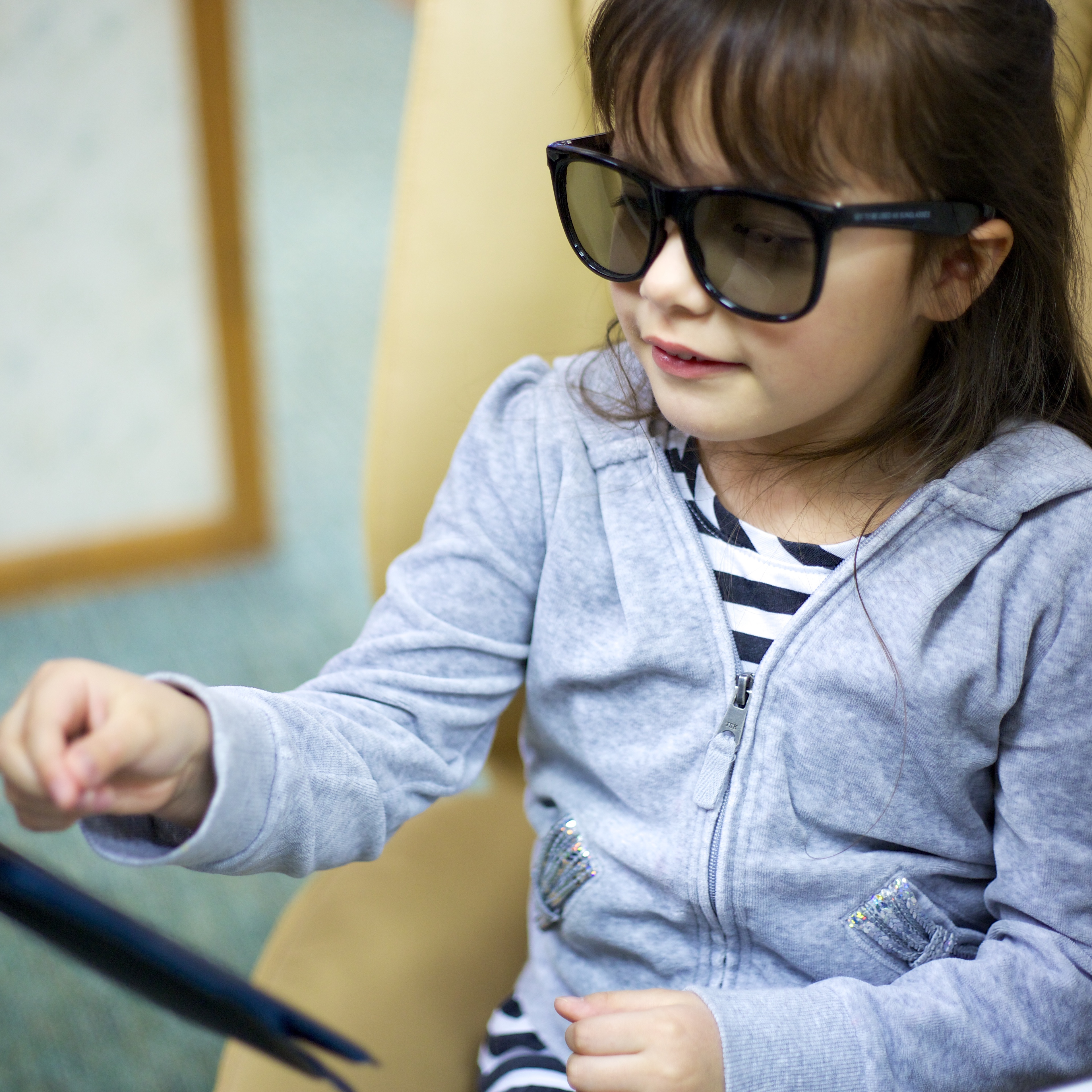

Children's Vision
It's extremely important to discover any eye issues in children as young as possible. At Hamilton Eyecare Center, we can examine children of any age, including infants.
School screenings provide less than 4% of the information generated during a comprehensive eye exam and they miss up to 75% of children with vision problems. For more information, click here.
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Accommodative Dysfunction | An eye focusing problem that is unrelated to aging changes in the lens of the eye. |
| Amblyopia | See Lazy Eye |
| Astigmatism | A vision condition that causes blurred vision due either to the irregular shape of the cornea, the clear front cover of the eye, or sometimes the curvature of the lens inside the eye. |
| Blepharitis | An inflammation of the eyelids and eyelashes causing red, irritated, itchy eyelids and the formation of dandruff like scales on eyelashes. |
| Cataract | A cloudy or opaque area in the normally clear lens of the eye. |
| Chalazion | A slowly developing lump that forms due to blockage and swelling of an oil gland in the eyelid. |
| Color Vision Deficiency | The inability to distinguish certain shades of colors or, in more severe cases, see colors at all. |
| Computer Vision Syndrome | A group of eye and vision-related problems that result from prolonged computer use. |
| Conjunctivitis | An inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, the thin transparent layer of tissue that lines the inner surface of the eyelid and covers the white part of the eye. |
| Convergence Insufficiency | An eye coordination problem in which the eyes have a tendency to drift outward when reading or doing close work. |
| Corneal Abrasion | A cut or scratch on the cornea, the clear front cover of the eye. |
| Crossed Eyes | A condition in which both eyes do not look at the same place at the same time. |
| Diabetic Retinopathy | A condition occurring in persons with diabetes, which causes progressive damage to the retina, the light sensitive lining at the back of the eye. |
| Dry Eye | A condition in which there are insufficient tears to lubricate and nourish the eye. |
| Farsightedness | A vision condition in which distant objects are usually seen clearly, but close objects do not come into proper focus. |
| Floaters & Spots | The shadowy images that are seen moving in your field of vision caused by particles floating in the fluid that fills the inside of the eye. |
| Glaucoma | A group of disorders leading to progressive damage to the optic nerve, and is characterized by loss of nerve tissue resulting in loss of vision. |
| Hordeolum | See Sty |
| Hyperopia | See Farsightedness |
| Keratitis | An inflammation or infection of the cornea, the clear front cover of the eye. |
| Keratoconus | An eye disorder causing progressive thinning and bulging of the cornea, the clear front cover of the eye. |
| Lazy Eye | The loss or lack of development of clear vision in just one eye. It is not due to eye health problems and eyeglasses or contact lenses can’t fully correct the reduced vision caused by lazy eye. |
| Learning-related Vision Problems | Vision disorders that interfere with reading and learning. |
| Macular Degeneration | An eye disease affecting the macula, the center of the light sensitive retina at the back of the eye, causing loss of central vision. |
| Migraine with Aura | See Ocular Migraine |
| Myopia | See Nearsightedness |
| Nearsightedness | A vision condition in which you can see close objects clearly, but objects farther away are blurred. |
| Nystagmus | A vision condition in which the eyes make repetitive, uncontrolled movements, often resulting in reduced vision. |
| Ocular Allergies | The abnormal response of sensitive eyes to contact with allergens and other irritating substances. |
| Ocular Hypertension | An increase in the pressure inside the eye above the range considered normal, without any detectable changes in vision or damage to the structures of the eye. |
| Ocular Migraine | A type of severe headache accompanied by various visual symptoms. |
| Pinguecula | An abnormal growth of tissue on the conjunctiva, the clear membrane that covers the white of the eye. |
| Presbyopia | An age-related vision condition in which there is a gradual loss of the eye’s ability to focus on near objects. |
| Pterygium | An abnormal growth of tissue on the conjuctiva, the clear membrane that covers the white of the eye, and the adjacent cornea, the clear front surface of the eye. |
| Ptosis | A drooping of the upper eyelid. |
| Retinal Detachment | A tearing or separation of the retina, the light sensitive lining at the back of the eye, from the underlying tissue. |
| Retinitis Pigmentosa | A group of inherited disorders of the retina, the light sensitive lining at the back of the eye, which cause poor night vision and a progressive loss of side vision. |
| Retinoblastoma | A rare type of eye cancer occurring in young children that develops in the retina, the light sensitive lining at the back of the eye. |
| Strabismus | See Crossed Eyes |
| Sty | An infection of an oil gland in the eyelid. |
| Subconjunctival Hemorrhage | An accumulation of blood underneath the conjunctiva, the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye. |
| Uveitis | An inflammation of one or more of the structures that make up the middle layer of the eye called the uvea. |